Have you ever wondered what happens when a product gets returned, repaired, or recycled? That is where reverse logistics comes in. It is the process of managing the backward flow of goods in the supply chain, and in E-commerce fulfillment, return rates can reach 20 to 30% making it a key part of warehouse management systems, last mile delivery, and 3PL logistics.
Smart supply chain companies are now turning to advanced reverse logistics solutions to save costs, recover value, and keep customers happy. By understanding the difference between SCM vs logistics, businesses can create supply chains that are not only efficient but also sustainable, turning returns and reverse flows into real opportunities.
What Is Reverse Logistics?
Reverse logistics is the process of moving products from the customer back through the supply chain for returns, repairs, recycling, or disposal. Unlike traditional logistics, it focuses on what happens after a product is sold.
By integrating reverse logistics solutions with warehouse management systems, last mile delivery, and 3PL logistics, supply chain companies can reduce costs, recover value, and improve customer satisfaction. Understanding SCM vs logistics helps businesses build smarter and more sustainable supply chains.
How Reverse Logistics Works: Step-by-Step Process
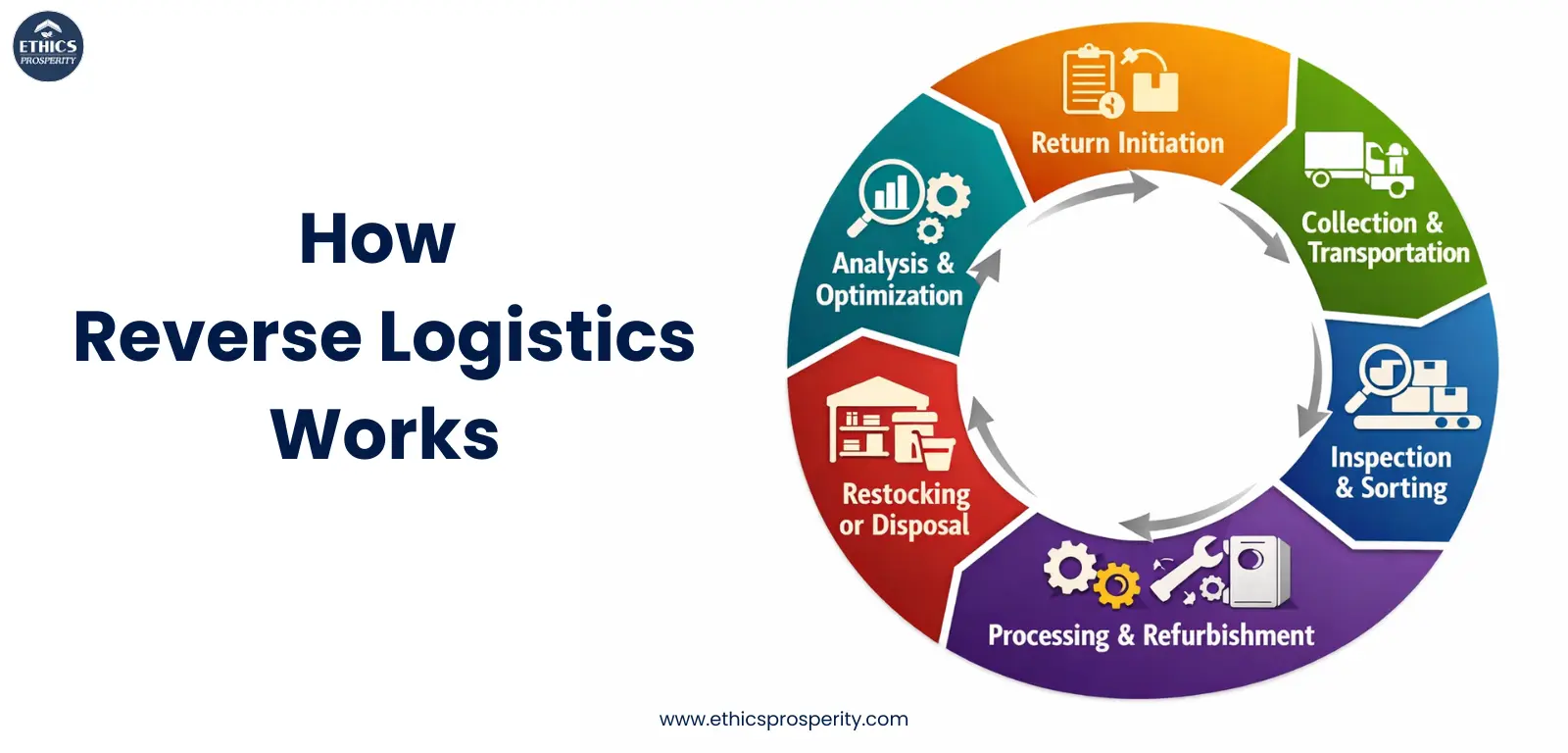
Reverse logistics involves several key steps that ensure returned or end-of-life products are handled efficiently and sustainably. Here’s a simple breakdown:
-
Return Initiation – Customers initiate returns or repairs through the retailer or E-commerce fulfillment platform. Clear policies make this process seamless.
-
Collection & Transportation – Returned products are collected and moved via last mile delivery or 3PL logistics networks to warehouses or service centers.
-
Inspection & Sorting – Items are checked for damage, usability, or warranty claims. Products are sorted for resale, refurbishment, recycling, or disposal.
-
Processing & Refurbishment – Usable products may be repaired or refurbished, creating additional value for supply chain companies.
-
Restocking or Disposal – Products that can be reused are added back to inventory in the warehouse management system, while others are responsibly recycled or disposed of following regulations.
-
Analysis & Optimization – Data from returns is analyzed to improve operations, reduce costs, and refine reverse logistics solutions.
Following this structured process helps businesses save costs, enhance customer satisfaction, and strengthen their overall supply chain. Understanding SCM vs logistics ensures that reverse logistics is integrated efficiently with forward logistics operations.
Real-World Reverse Logistics Examples
Reverse logistics can be observed in everyday business operations, demonstrating its adaptability across industries. A strong example is Home Depot, where reverse logistics plays a critical role in E-commerce fulfillment. Customers can return products through shipping or in-store drop-off options, supported by efficient last mile delivery and centralized warehouse management systems. These reverse logistics solutions help process damaged or misdirected items quickly, enabling supply chain companies to maintain a smooth and customer-centric return experience.
In the textile sector, Levi Strauss showcases how reverse logistics supports sustainability. Returned jeans are collected, sorted, and repurposed through advanced reverse logistics solutions, with usable fibers reprocessed into raw materials. By integrating reverse logistics into broader operations, the company demonstrates the strategic value of SCM vs logistics, balancing operational efficiency with environmental responsibility.
These real-world examples highlight how reverse logistics, supported by 3PL logistics, warehouse management systems, and last mile delivery, helps businesses manage returns, reduce waste, and build sustainable supply chains across diverse industries.
Why Reverse Logistics Is Important in Modern Supply Chains
Reverse logistics has become a strategic necessity as global supply chains grow more complex and return volumes increase. Studies show that returns can account for nearly 10% of total supply chain costs, making efficient reverse logistics solutions critical for cost control and operational efficiency. In E-commerce fulfillment, streamlined reverse logistics supports faster processing, reduces inventory losses, and strengthens last mile delivery performance.
For supply chain companies and 3PL logistics providers, integrating reverse logistics with warehouse management systems improves inventory accuracy by up to 20% and enables better recovery of reusable or resalable products. It also supports sustainability goals, as effective reverse flows can reduce landfill waste by 15 to 25% Understanding SCM vs logistics helps organizations align reverse operations with broader supply chain strategies, transforming returns into value and building resilient, future-ready supply chains.
Best Practices for an Efficient Reverse Logistics Strategy
With rising return volumes and growing sustainability expectations, adopting best practices in reverse logistics is essential for building resilient and cost-efficient supply chains. Some of the best practices are:
1. Simplify and Standardize Return Policies
Clear and consistent return policies are critical for effective reverse logistics in India’s growing E-commerce fulfillment market.
-
Simple and Transparent Guidelines
Clearly communicate return timelines, eligibility criteria, and instructions to reduce confusion and unnecessary returns. -
Flexible Return Channels
Offer doorstep pickups, in-store returns, and local drop-off points to improve convenience and optimize last mile delivery.
Example: Flipkart
Flipkart enables easy app-based return initiation supported by strong last mile networks and integrated warehouse management systems.
2. Implement Efficient Return Processing Systems
Efficient processing ensures faster turnaround and better cost control.
-
Automation and Centralization
Use technology-driven reverse logistics solutions and centralized return hubs to streamline inspection, sorting, and inventory updates. -
Real-Time Visibility
Track returned items in real time to improve coordination with 3PL logistics partners and internal teams.
Example: Amazon India
Amazon India processes high return volumes using automated systems and centralized facilities to maintain speed and inventory accuracy.
3. Optimize Transportation and Logistics Networks
Transportation efficiency directly impacts reverse logistics costs.
-
Shipment Consolidation
Combine multiple return consignments to minimize transportation costs and streamline routing. -
Specialized 3PL Partnerships
Collaborate with experienced 3PL logistics providers to manage scale and regional complexity.
Example: Delhivery
Delhivery offers dedicated reverse logistics services across India, helping supply chain companies streamline return transportation.
4. Enhance Product Recovery and Resale
Recovering value from returned goods improves profitability and sustainability.
-
Inspection and Refurbishment
Assess returned items for resale, repair, or refurbishment before disposal. -
Responsible Recycling
Recycle non-reusable products in compliance with environmental regulations.
Example: Reliance Retail
Reliance Retail integrates refurbishment, redistribution, and recycling into its reverse logistics operations.
5. Leverage Data Analytics for Continuous Improvement
Data-driven insights strengthen reverse logistics performance over time.
-
Return Trend Analysis
Analyze return reasons and product performance to reduce repeat issues and avoidable returns. -
Inventory and Forecast Optimization
Use return data within warehouse management systems to improve inventory planning and forecasting accuracy.
Example: Tata Group Retail Businesses
Tata retail brands use analytics to optimize returns, inventory, and overall efficiency, highlighting the importance of SCM vs logistics alignment.
Future of Reverse Logistics: A Supply Chain Leader’s View
Reverse logistics is evolving from a support function into a strategic priority for modern supply chains. As return volumes rise and sustainability expectations grow, supply chain leaders are recognizing reverse logistics as a key driver of efficiency, resilience, and long-term value
In India, the reverse logistics market is projected to expand from about USD 90.7 billion in 2024 to nearly USD 387.3 billion by 2033, reflecting strong growth in E-commerce fulfillment, commercial returns, and circular supply chain practices.
Technology will be a central force. Advanced warehouse management systems, automation, and data analytics will enable faster return processing, improved forecasting, and better decision-making, helping organizations shift from reactive handling to proactive planning. Sustainability will also drive change, with leaders adopting refurbishment, reuse, and recycling models to reduce waste and meet environmental goals.
Collaboration with 3PL logistics providers and strong last mile delivery networks will help scale reverse logistics operations efficiently. From a leadership perspective, integrating reverse logistics into broader strategy and clearly understanding SCM vs logistics will be essential to turning returns into competitive advantage and building resilient, future-ready supply chains.
Conclusion
Reverse logistics is a key driver of efficiency and sustainability in modern supply chains. From E-commerce fulfillment and last mile delivery to advanced warehouse management systems and reverse logistics solutions, businesses are rethinking how returns are managed. As the line between SCM vs logistics becomes clearer, supply chain companies and 3PL logistics providers are embedding reverse logistics into core strategies.
At Ethics Prosperity, technology, transparency, and principled practices come together to build resilient supply chains that create long-term value and trust.